A Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) is an infection that occurs in any part of the urinary system, which includes the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. Most UTIs involve the lower urinary tract — the bladder and the urethra. 
Urinary Tract Infection (UTI):
- Cause: UTIs are usually caused by bacteria, most commonly Escherichia coli (E. coli), which live in the bowel. These bacteria can enter the urinary tract through the urethra and multiply in the bladder.
- Types: UTIs can be classified based on the part of the urinary system that is infected:
- Cystitis (bladder infection): The most common type of UTI, causing inflammation of the bladder.
- Urethritis (urethra infection): Infection of the urethra.
- Pyelonephritis (kidney infection): A more serious infection that affects the kidneys.
Common Symptoms: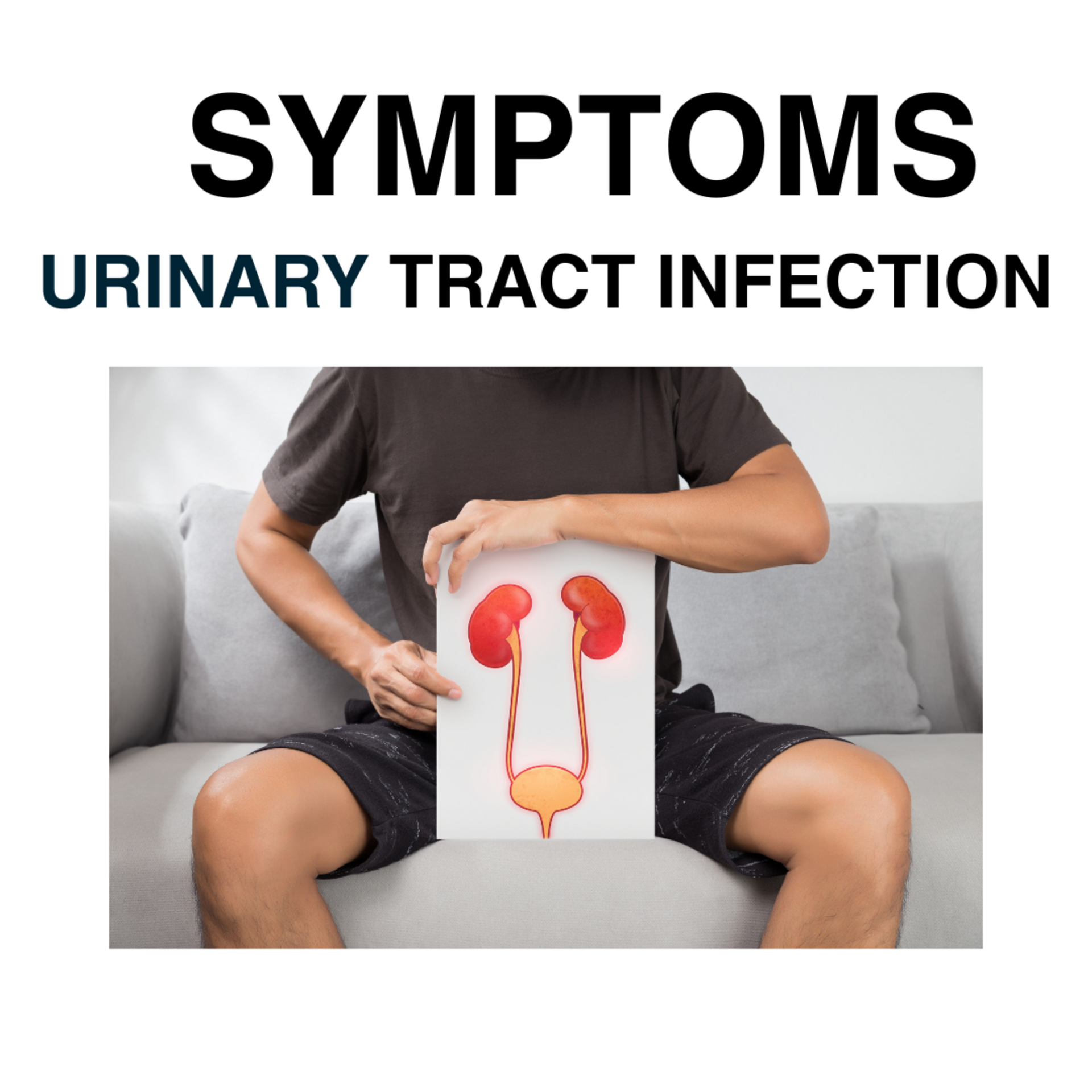
- Dysuria: Pain or a burning sensation when urinating.
- Frequency: An increased need to urinate, often passing small amounts of urine.
- Urgency: A strong, persistent urge to urinate.
- Cloudy Urine: Urine that appears cloudy or has a strong odor.
- Hematuria: Blood in the urine, which may appear red, bright pink, or cola-colored.
- Pelvic Pain: Discomfort or pressure in the lower abdomen, especially around the pubic bone.
Symptoms of Upper UTI (Kidney Infection):
- Flank Pain: Pain in the back or side, below the ribs.
- Fever and Chills: Often accompany kidney infections.
- Nausea and Vomiting: Can occur with more severe infections.
- General Malaise: Feeling unwell, fatigued, or weak.
Causes of UTI
Bacterial Entry:
- E. coli: The most common bacterium causing UTIs, typically originating from the gastrointestinal tract.
- Other Bacteria: Include Staphylococcus saprophyticus, Proteus mirabilis, and Klebsiella pneumoniae.
Risk Factors:
- Female Anatomy: Women are at higher risk due to a shorter urethra, allowing bacteria easier access to the bladder.
- Sexual Activity: Increased sexual activity can introduce bacteria into the urinary tract.
- Menopause: Reduced estrogen levels can alter the urinary tract environment, increasing the risk of infection.
- Urinary Catheters: Long-term catheter use can introduce bacteria into the urinary tract.
- Immune Suppression: Conditions like diabetes or medications that weaken the immune system can increase susceptibility to UTIs.
Treatment of UTI

Antibiotic Therapy:
- Consult Urologist
Hydration:
- Increased Fluid Intake: Drinking plenty of water helps flush out the bacteria from the urinary tract.
Prevention:
- Hygiene Practices: Proper wiping techniques and urinating after intercourse to prevent bacterial entry.
- Cranberry Products: Some evidence suggests cranberry juice or supplements can reduce the risk of UTIs.
- Probiotics: Can help maintain a healthy balance of bacteria in the urinary tract.
Recurrent UTI Management:
- Prophylactic Antibiotics: Low-dose antibiotics may be prescribed for an extended period for individuals with frequent UTIs. However it is always advisable to visit Urologist near you. You can consult Dr. Bhoopat if you are looking for Urologist in Pune.
- Specialized Testing: To identify underlying conditions predisposing to frequent infections.
When to Seek Medical Attention
- Severe Symptoms: Such as high fever, flank pain, nausea, and vomiting.
- Recurrent Infections: Multiple UTIs within a short period.
- Pregnancy: UTIs during pregnancy require prompt medical attention to avoid complications.
In summary, UTIs are common but treatable infections of the urinary system. Early recognition of symptoms, timely treatment, and preventive measures are crucial for managing and reducing the risk of these infections.
Did you find this topic helpful?